What's Inside
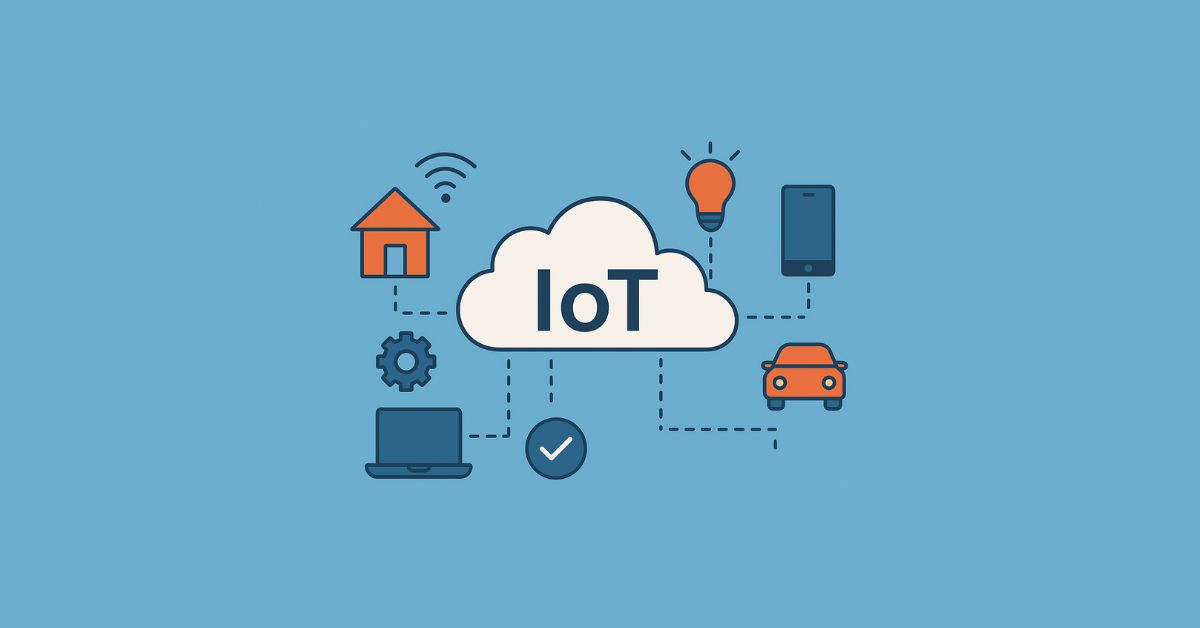
We now live in an era where homes, cities, and organizations function through the Internet of Things (IoT). It has transitioned from a concept in the future to an actual reality. Smart decision-making, predictive analytics, and automation are all driven by real-time data now available from billions of devices connected to the internet.
The Internet of Things is one of the most revolutionary technologies of our time. Businesses now have the chance to engage customers and innovate all in one. However, to understand it and all of its intricacies, the definition, functions, types, and practical uses of IoT across different industries need to be explained. Therefore, in this guide, we will outline the benefits and the challenges that need to be considered, too.
- Types of IoT Definations Uses of Iot
- How IoT Works: The Architecture
- Types of Internet of Things (IoT)?
1. Consumer IoT (CIoT)
2. Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
3. Commercial IoT
4. Infrastructure IoT - IoT Development Tools
- Key Uses of IoT Across Industries
- Benefits of IoT for Businesses
- Challenges in IoT Adoption
- Overcoming These Challenges
- Roadmap for Businesses to Adopt IoT
- Final Thoughts
- FAQs
What Is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
Back in the day, it used to be a misconception that IoT pertained only to smart devices like smart speakers, robotics, or any advanced machinery like supply chains or connected industrial systems. Turns out it is much more than that. It is a network of physical devices enabled with sensors, processors, and features that permit data collection and sharing.
At its core, IoT enables:
- Data Collection – Gathering temperature, health metrics, and motion in real life is now possible.
- Data Transmission – Transferring data through a network is now a breeze with information being securely collected.
- Processing and Analysis – Devices are now remote control powered, capable of gathering and analyzing the collected data to find insights.
- Action – Automated actions are triggered, or actionable insights are provided to decision-makers.
Real-World Example
Consider a smart thermostat in a home. It collects data about room temperature, adjusts heating/cooling automatically, and allows remote control via a mobile app. On a larger scale, factories use IoT to monitor machinery in real time, predict failures, and reduce downtime.
Why It Matters for Businesses
- Real-time monitoring improves operational efficiency.
- Predictive analytics helps reduce downtime and maintenance costs.
- Connected systems create new customer experiences and revenue models.
For businesses considering digital transformation, IoT is not optional — it is foundational.
How IoT Works: The Architecture
IoT systems typically follow a four-layer architecture:
1. Perception Layer (Devices & Sensors)
- Includes sensors, RFID tags, GPS, cameras, and actuators.
- Function: Collect data from the physical environment.
2. Network Layer (Connectivity)
- Transfers data using Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, 5G, or LPWAN.
- Function: Secure communication between devices and servers.
3. Processing Layer (Data Management)
- Uses cloud platforms, edge computing, and AI/ML algorithms.
Function: Store, process, and analyze large volumes of IoT data.
4. Application Layer (User Interaction)
- Provides actionable insights through dashboards, apps, or alerts.
- Function: Enables end-users to monitor, control, and optimize processes.
This layered approach ensures IoT systems are scalable, secure, and adaptable across industries.
Types of Internet of Things (IoT)?
IoT applications can be organized into many different groups depending on what they are used for and what industry players are working in.
1. Consumer IoT (CIoT)
This is the area that deals with devices that people use in their everyday lives. The devices are meant for easy to use, smart, entertaining, tracking health, and controlling the home system.
Examples:
- Smart home appliances (smart TVs, refrigerators, washing machines).
- Wearable devices (fitness trackers, smartwatches, AR/VR headsets).
- Voice assistants (Amazon Alexa, Google Home, Apple HomePod).
- Smart security systems (doorbell cameras, smart locks).
Use Cases:
- Health monitoring: Smartwatches track heart rate, oxygen levels, and sleep cycles, alerting users to potential health concerns.
- Home automation: Devices like smart thermostats and lighting systems optimize energy usage.
- Entertainment: Connected TVs and speakers enhance user experience through integrated apps and services.
Impact: Consumer IoT empowers individuals with real-time data and smarter living environments, but it also raises concerns about data privacy and security.
2. Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
This is the area that deals with the Internet of Things with the focus of manufacturing, logistics, and industry. The devices allow to make predictive maintenance work, control supply chain, and monitor the machines in real time.
Examples:
- Sensors on factory machinery for condition monitoring.
- Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) in warehouses.
- Smart meters and energy monitoring devices in power plants.
Use Cases:
- Predictive maintenance: Machines equipped with IoT sensors detect potential failures before they occur, reducing costly downtime.
- Process automation: Connected assembly lines adjust production flow automatically based on demand.
- Supply chain visibility: RFID tags and GPS tracking provide real-time location data of shipments.
Impact: IIoT is a key driver of Industry 4.0, enabling smarter factories, reduced operational costs, and improved worker safety.
3. Commercial IoT
Healthcare, retail and hospitality sectors, as well as office space, employ Commercial IoT. This is where the gaps between consumer and Industrial IoT is infused, that is, subnetworks of organizations which directly connect to users and take feedback. Things of value such as:
Examples:
- Smart hospital equipment (remote patient monitoring systems, connected ventilators).
- Retail IoT solutions (smart shelves, automated checkout systems).
- Smart office systems (connected HVAC, energy-efficient lighting, occupancy sensors).
Use Cases:
- Healthcare: IoT-enabled medical devices track patient vitals in real-time, sending data to doctors remotely.
- Retail: Smart shelves monitor inventory and alert staff when restocking is needed.
- Workplaces: IoT-driven smart offices optimize air quality, lighting, and energy consumption.
Impact: Commercial IoT enhances customer experiences, ensures safety in public spaces, and helps organizations become more efficient and responsive.
4. Infrastructure IoT
IoT in infrastructure looks at the set up and development of services in the city and country. Projects of this nature are usually initiated by the government or other major organizations in the city for the betterment of the public services, safety, and sustainability.
Examples:
- Smart traffic lights and connected road sensors.
- IoT-enabled bridges, dams, and railway systems for structural monitoring.
- Smart grids for energy distribution.
- Waste management systems with sensor-equipped bins.
Use Cases:
- Smart cities: IoT sensors manages, tracks, and controls the movement of vehicles in the city, reduces traffic, and improves the overall response time for emergencies in and around the city.
- Structural monitoring: Sensors in bridges or in tunnels are placed to monitor and notify if there are early signs of repairs needed.
- Energy optimization: Control and management of energy using smart grids helps to dynamically balance the distribution of electricity to various areas.
Impact: Infrastructure IoT helps to improves the safety, efficiency, and the sustainability of cities. Helps to control and manage the pollution, urban congestion, and public safety.
IoT Development Tools
Building IoT solutions requires a combination of hardware platforms, software frameworks, and cloud services. The right tools make it easier to design, test, and scale IoT systems. Some widely used IoT development tools include:
Arduino
A popular open-source electronics platform used to prototype IoT devices. Arduino boards and its programming environment are ideal for beginners and small-scale projects.Raspberry Pi
A versatile microcomputer that supports advanced IoT projects. It’s widely used for edge computing, home automation, and AI-enabled IoT applications.Node-RED
A flow-based development tool that simplifies connecting devices, APIs, and services. It is often used for rapid prototyping and integration in IoT systems.Kaa IoT Platform
An end-to-end IoT platform for device management, data collection, and analytics. It helps businesses scale IoT deployments efficiently.IBM Watson IoT
A cloud-based service that integrates AI and IoT. It allows real-time device monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven insights.AWS IoT Core
Amazon’s managed cloud platform that connects billions of devices securely. It’s popular for enterprises that need scalability and robust security features.
👉 For a deeper dive into these and more, you can check out our detailed blog on IoT Development Tools (insert internal link).
Key Uses of IoT Across Industries
Each industry has its own Internet of Things or IoT applications. IoT is not limited to one sector.
Manufacturing
- Smart machines that can automatically detect problems.
- The manufacturing industry can utilize supply chain business networks with real-time tracking.
Retail
- Smart shelves with automatic inventory tracking.
- IoT beacons can be used to identify and customize users’ shopping experiences.
Transportation and Logistics
- Management of fleets using GPS tracking.
- Sending real time updates to customers regarding their orders.
Agriculture
- Irrigation systems that monitor soil moisture levels.
- Crop monitoring using drones.
Smart Cities
- Public waste management, lighting and other connected infrastructure.
- City traffic systems.
Benefits of IoT for Businesses
Here IoT use cases that improves business operations in the following ways:
1. Operational Efficiency
- Automates repetitive tasks.
- Reduces manual errors and downtime.
2. Real-Time Data Insights
- Enables predictive analytics.
- Improves decision-making accuracy.
3. Cost Savings
- Optimizes energy usage.
- Reduces maintenance and labor costs.
4. Enhanced Customer Experience
- Offers personalized products and services.
- Builds long-term customer loyalty.
5. Scalability
- IoT ecosystems can grow with business needs.
Challenges in IoT Adoption
Despite the benefits, IoT implementation comes with challenges:
- Security Risks – Each connected device can be a vulnerability point.
- Data Overload – Handling massive data requires robust cloud/edge systems.
- Integration Issues – Legacy IT systems may not align with IoT.
- High Initial Costs – Infrastructure, sensors, and deployment require investment.
Overcoming These Challenges
- Use end-to-end encryption and strong authentication.
- Choose scalable cloud/edge solutions.
- Partner with an experienced IoT solutions provider for seamless integration.
Roadmap for Businesses to Adopt IoT
If your business is considering IoT, follow a structured approach:
- Define Objectives – Identify goals such as cost reduction, customer engagement, or automation.
- Start Small – Begin with pilot projects before scaling.
- Choose the Right Platform – Select IoT platforms that support scalability and analytics.
- Prioritize Security – Implement strong device authentication and encrypted communication.
- Integrate with Existing Systems – Ensure IoT works with ERP, CRM, or other enterprise platforms.
- Measure ROI – Regularly analyze cost savings, efficiency gains, and customer benefits.
Working with a professional IoT development company ensures businesses get secure, scalable, and customized solutions.
Final Thoughts
The Internet of Things is transforming industries by connecting devices, generating insights, and enabling smarter decisions. For businesses, IoT is not just a technology investment but a strategic enabler of digital transformation.
If you’re considering implementing IoT in your business, explore our IoT Development Services to build secure, scalable, and future-ready solutions.
FAQs
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of physical devices like sensors, appliances, and machines that connect to the internet to share data and perform tasks without much human effort.
IoT focuses on consumer and general business use, while IIoT applies to industrial and manufacturing settings with more robust connectivity and data systems.
Popular IoT tools include Arduino, Raspberry Pi, Node-RED, Kaa IoT, AWS IoT Core, and IBM Watson IoT. These help developers build, connect, and manage IoT devices and applications effectively.
The main types of IoT are Consumer IoT (CIoT), Industrial IoT (IIoT), Commercial IoT, and Infrastructure IoT. Each serves different purposes, from smart homes to manufacturing and large-scale city management.
IoT can be secure if best practices such as device authentication, encrypted communication, and regular software updates are followed.
Manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, and smart cities are among the top adopters.
The best starting point is a consultation with an IoT solutions provider to assess needs, define goals, and design a scalable architecture.