What is Data Analytics? How It Works, Types, Importance, Techniques, Example & Future Trends


Data Analytics has become the backbone of successful digital businesses, driving smarter decisions across industries and shaping the way organizations understand their customers, operations, and markets. In today’s data-driven world, harnessing analytics is not just a competitive advantage—it’s a necessity for growth, innovation, and agility. From healthcare and finance to retail and manufacturing, companies are unlocking actionable insights that help them optimize processes, predict outcomes, and deliver better customer experiences.
But what exactly is data analytics, and why is it such a game-changer? This comprehensive guide will take you from the foundations to the advanced applications and future trends, offering a roadmap for anyone looking to leverage analytics, whether you’re a business leader, aspiring analyst, or curious learner.
Data Analytics is the systematic process of examining raw data to uncover patterns, trends, and insights that inform decision-making. It combines statistical analysis, computer science, and domain expertise to transform complex datasets into meaningful intelligence. The process encompasses steps like data collection, cleaning, modeling, interpretation, and visualization, ensuring organizations extract maximum value from their information assets.
Data analytics goes far beyond just numbers—in modern enterprises, it’s closely linked to strategic planning, customer personalization, risk management, and overall operational excellence. By analyzing historical and real-time data, organizations can forecast trends, identify inefficiencies, and even automate routine tasks with confidence.
Data analytics is a structured process with multiple stages, ensuring that data is reliable and that the insights generated are valuable. Each step plays a specific role in turning raw data into usable knowledge.
Gathering data from multiple sources such as databases, CRM systems, web platforms, IoT devices, and external feeds. This raw data can be structured (e.g., sales records) or unstructured (e.g., social media posts).
Exceptional analytics depend on quality data. Cleaning involves removing duplicates, handling missing values, correcting errors, and formatting for consistency—often the most time-consuming yet crucial stage.
Data is standardized, categorized, and merged to create a comprehensive, analyzable dataset, making it easier to compare variables and identify relationships.
Analysts apply statistical methods, machine learning algorithms, or domain-specific models to extract insights, spot trends, and make predictions.
Analytics without communication are useless. Insights need to be clearly presented using dashboards, charts, and reports that enable stakeholders to make informed decisions.
The final findings drive decisions—whether it’s specific campaigns, business process changes, or new product launches.
This cyclical process creates a feedback loop — new data continuously enters the pipeline, generating ongoing opportunities for insight.
There are four major types of data analytics, each serving distinct business objectives:
Descriptive analytics focuses on understanding past data to explain “What happened?” It uses dashboards, charts, and reports to summarize trends and provide a clear picture of historical performance.
Diagnostic analytics digs deeper into past data to answer “Why did it happen?” By identifying correlations, patterns, and root causes, it provides context behind events or results.
Predictive analytics uses models, statistics, and machine learning to answer “What is likely to happen?” It allows organizations to forecast trends, customer behavior, and risks with greater accuracy.
Prescriptive analytics goes beyond predictions by answering “What should we do?” It recommends actions and strategies based on predictive insights, often using AI-powered simulations.

Related To Read
Data analytics is the practice of examining and interpreting data to uncover insights, trends, and relationships that drive better decision-making. By applying statistical and computational methods, organizations can turn raw information into meaningful intelligence. The use of data analytics empowers businesses to optimize processes, understand customers, detect risks, and stay competitive in a rapidly changing environment.
Data analytics helps organizations pinpoint inefficiencies and identify opportunities to streamline operations. From production and inventory management to supply chain logistics, businesses can optimize workflows, reduce delays, and improve overall performance.
Analyzing customer data reveals insights into preferences, purchasing habits, and demographics. These insights allow organizations to personalize marketing campaigns, enhance customer engagement, and strengthen brand loyalty.
By studying product usage patterns and customer feedback, companies can better understand what works and what doesn’t. This information guides product improvements, feature updates, and innovation in design and development.
Data analytics plays a vital role in preventing fraudulent activities. Advanced models can detect unusual patterns in transactions, helping businesses combat issues like credit card fraud, insurance fraud, and identity theft.
Analyzing resource utilization and operational data enables organizations to identify wasteful spending and unnecessary expenses. With these insights, companies can cut costs, allocate resources more efficiently, and boost profitability.
Overall, the use of data analytics provides organizations with actionable insights that lead to smarter strategies, improved outcomes, and long-term competitiveness.
The methods of data analytics define how organizations approach their data to gain useful results. Each technique is suited for specific types of problems and data sets.
Statistical analysis uses mathematical models and formulas to interpret and summarize data. It helps reveal patterns, averages, and correlations that guide decisions.
Data mining is the process of discovering hidden patterns, connections, and relationships in large datasets. It is widely used in industries like retail and finance.
Machine learning and AI apply algorithms that can learn from data, detect anomalies, and make predictions automatically. These techniques are key to advanced analytics.
Text analytics extracts insights from unstructured text data such as reviews, emails, or social media posts. It helps measure sentiment, detect trends, and monitor brand reputation.
Data visualization converts complex datasets into charts, graphs, and dashboards, making it easier for users to interpret results and communicate findings.
A/B testing compares two or more variations of a product, campaign, or feature to identify which one performs better. It’s commonly used in marketing and product design.
Data analytics has become a core part of nearly every industry, enabling organizations to optimize operations, understand customers, and create new opportunities. Data analytics applications range from business intelligence to fraud detection, making it a versatile tool for both strategy and innovation. For instance, an example of data analytics can be seen in how retailers use customer insights to personalize shopping experiences and improve sales.
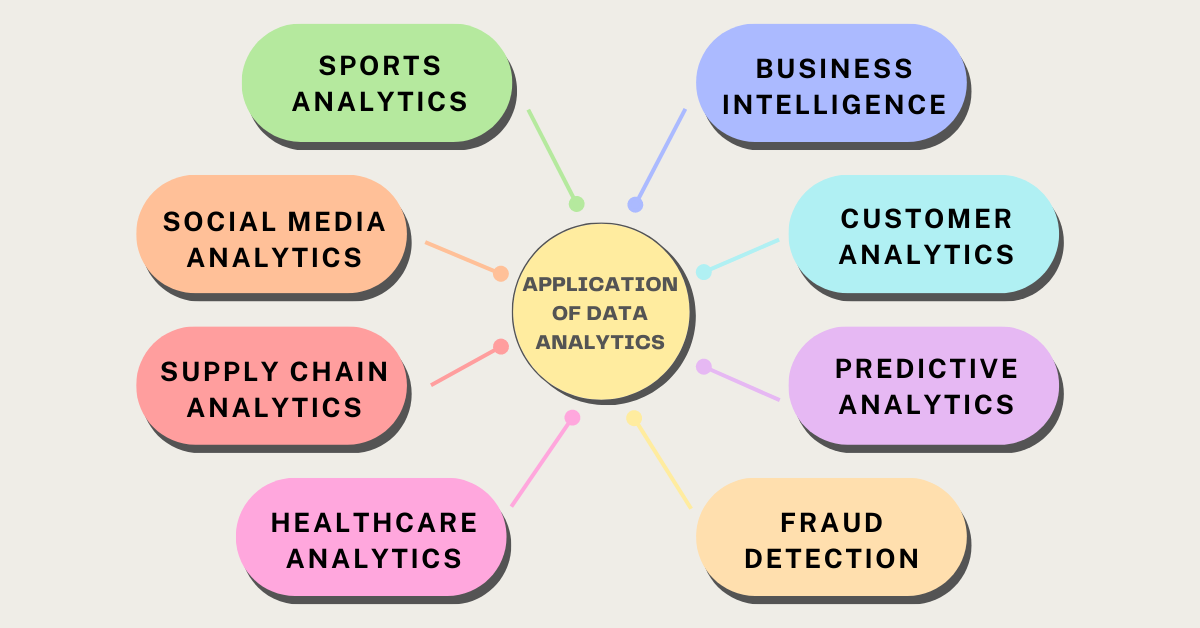
Business intelligence relies on data analytics to provide organizations with clear insights into their operations. By analyzing data from different sources, companies can uncover patterns, trends, and correlations that help improve decision-making, boost performance, and stay ahead of competitors.
Customer analytics focuses on understanding customer behavior, preferences, and demographics. By analyzing this data, businesses can personalize offerings, improve customer engagement, and build long-term loyalty through targeted marketing strategies.
Predictive analytics uses historical and current data to forecast future outcomes. By identifying patterns and trends, businesses can anticipate demand, predict risks, and plan strategies for better performance of products and services.
Data analytics plays a crucial role in identifying suspicious activities. By analyzing transaction patterns and anomalies, organizations can detect and prevent fraud in areas like banking, insurance, and e-commerce before it causes significant damage.
In healthcare, data analytics helps improve patient care, optimize medical processes, and enhance efficiency. It enables predictive modeling for disease outbreaks, personalized treatment plans, and fraud detection within healthcare systems.
Analytics strengthens supply chain operations by revealing inefficiencies, forecasting demand, and improving inventory management. Companies can reduce delays, cut costs, and respond more effectively to changes in market conditions.
Social media platforms generate massive amounts of data daily. With analytics, businesses can measure engagement, track audience sentiment, and identify what type of content performs best. This helps optimize campaigns for maximum impact.
Sports teams use data analytics to improve performance, refine strategies, and monitor player health. By analyzing player statistics, tracking movements, and reviewing game footage, coaches and managers make more informed decisions.
Overall, the applications of data analytics span across industries, helping organizations turn raw data into actionable insights. Whether in healthcare, business, or sports, analytics empowers smarter decision-making and creates a lasting competitive edge.
Data analytics has evolved from simple statistical methods into a sophisticated discipline powered by big data, advanced tools, and intelligent algorithms. What once involved basic reporting now includes predictive models, machine learning, and real-time insights. As technology continues to advance, the future of data analytics trends will be shaped by powerful innovations and new challenges that organizations must prepare for.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are set to play an even bigger role in data analytics. These technologies will enable automated decision-making, deeper pattern recognition, and highly accurate predictions, making analytics faster and smarter.
NLP will expand the scope of analytics by allowing systems to interpret and analyze human language. This means businesses can gain insights from unstructured data sources like emails, social media posts, and customer feedback more effectively.
The demand for real-time analytics will grow as businesses seek to act instantly on streaming data. Coupled with predictive modeling, organizations will not only understand what is happening but also anticipate what is likely to occur.
As analytics becomes more advanced, concerns around data privacy and security will intensify. Protecting sensitive information and ensuring compliance with regulations will be essential to maintain trust and credibility.
The future will also require stronger ethical guidelines to govern how analytics is applied. Organizations must ensure fairness, transparency, and accountability in their data practices to avoid bias and misuse.
In short, the future of data analytics is full of opportunities but also demands responsibility. Businesses that embrace innovation while addressing ethical and security concerns will be best positioned to thrive.
Data analytics is no longer just a competitive advantage — it’s a necessity. Organizations that invest in analytics capabilities are better equipped to understand their customers, predict trends, and make better business decisions. By following the processes, adopting the right techniques, and staying aware of future trends, businesses can leverage data analytics to unlock growth and efficiency.
If you’re ready to harness the power of data, explore our Data Analytics Services to see how we can help transform your business. Visit GrapesTech Solutions today and start making smarter, data-driven decisions.
Data analytics is the process of examining data to find patterns and insights that help make better decisions.
It helps organizations improve efficiency, make data-driven decisions, and stay competitive.
Examples include fraud detection in banking, personalized marketing campaigns, and predictive maintenance in manufacturing.
It involves data collection, cleansing, transformation, analysis, and visualization.
Data analytics focuses on analyzing existing data, while data science also includes building models, developing algorithms, and sometimes creating new data sources.
Skills include statistical knowledge, data visualization, SQL, Python or R programming, and critical thinking.
Data analytics Tools include Excel, Power BI, Tableau, SQL databases, Python, and R.
Industries include finance, healthcare, retail, logistics, sports, and technology.
It will become more automated, AI-driven, and accessible to non-technical users through no-code tools.