Introduction
The database world is facing its “iPhone moment.” For decades, accessing data required a specific, rigid skill set: knowing Structured Query Language (SQL). If you didn’t know the syntax, you didn’t get the data. But in 2026, that barrier is crumbling.
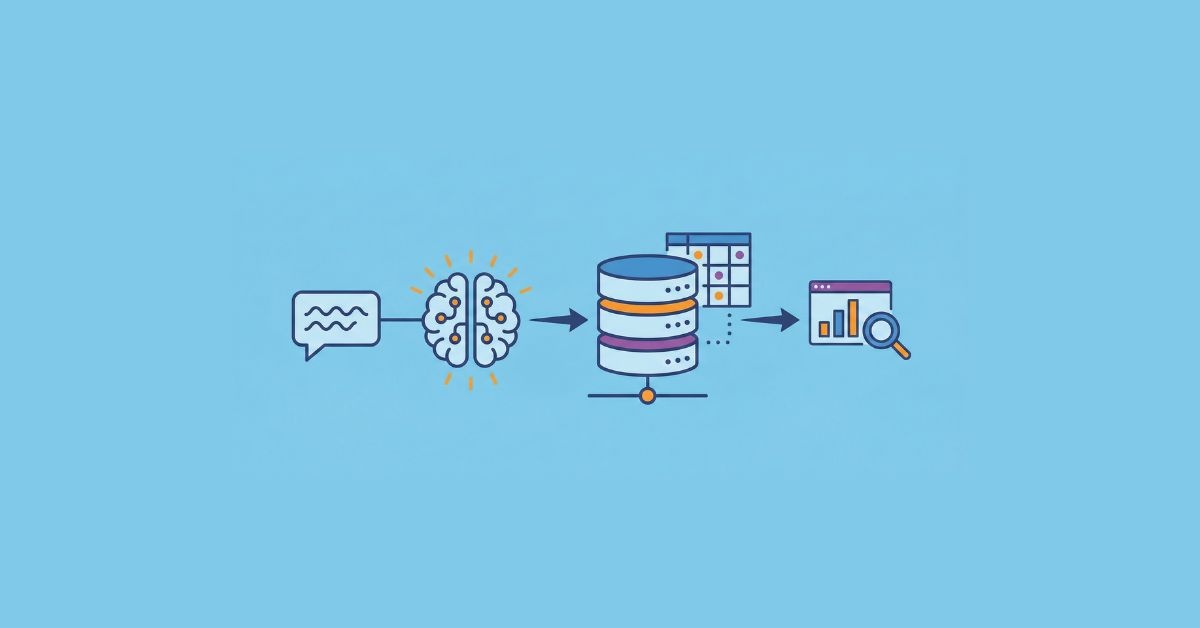
The rise of custom AI development has fundamentally transformed how we interact with data. We are moving from a world of rigid syntax to one of natural conversation. Text to SQL technology is making it possible for anyone—from CEOs to junior developers—to ask questions of their data in plain English and get precise, executable code in return.
This isn’t just about making things easier; it’s about making data accessible. In this guide, we will explore the explosive growth of text to sql llm technology, review the top SQL AI tools dominating the market, and discuss whether AI for SQL will replace database administrators or simply give them superpowers.
The Evolution: From Manual Queries to AI Assistants
To understand where we are going, we have to look at where we came from. Traditionally, writing SQL was a manual, error-prone process. A missing semicolon or a misspelled column name could crash a query.
The Old Way
Data Analysts spent 40% of their time just “finding” data—understanding schemas, figuring out table relationships, and writing complex JOIN statements. The “gatekeeper” model meant that business teams had to wait days for a simple report.
The New Way: SQL Using AI
Today, SQL using AI has flipped the script. Instead of manually constructing a query to find “total sales in Q3 for electronics,” a user simply types that phrase into a chat interface. The AI for SQL query engine interprets the intent, scans the database schema, and generates:
SELECT sum(sales_amount)
FROM sales
WHERE category = ‘electronics’
AND quarter = ‘Q3’;
This shift is powered by Large Language Models (LLMs) that have been trained on billions of lines of code. The result? A democratization of data that empowers non-technical users and accelerates technical workflows.
Deep Dive: How Text to SQL LLMs Work
It might seem like magic, but text to sql is built on sophisticated engineering. It’s not enough to just ask ChatGPT to ‘write a query.’ To work on enterprise data, you often need specialized AI development services to build a secure architecture.
1. The Role of LLMs
A text to sql llm is a language model fine-tuned specifically on database languages. General models like GPT-4 or Claude 3 are good, but specialized models (like those fine-tuned on the Spider dataset) are becoming the industry standard. They understand SQL syntax, dialects (PostgreSQL vs. MySQL), and complex logic like window functions.
2. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
This is the secret sauce. An AI for SQL tool doesn’t just “guess.” It uses RAG to look at your specific database schema (without seeing the actual sensitive data).
- Vector Embeddings: The tool converts your table names and column descriptions into vectors (numbers that represent meaning).
- Context Injection: When you ask a question, the system retrieves only the relevant table names and injects them into the prompt.
- Generation: The LLM generates the SQL based on your schema, not a generic one.
3. Self-Correction
The best SQL AI tools now have “self-healing” capabilities. If the generated SQL fails (e.g., due to a syntax error), the AI reads the error message, understands what went wrong, and automatically rewrites the query to fix it.
Top SQL AI Tools to Watch in 2026
The market is flooded with tools promising to automate your database work. Based on current trends and performance, here are the top contenders you should know.
1. SQLAI.ai
SQLAI.ai has emerged as a leader for its user-friendly interface. It focuses heavily on the ‘Text to SQL’ workflow, allowing users to connect to Postgres, MySQL, SQLite, or Snowflake. Its standout feature is the “Explain” button, which breaks down complex SQL into plain English so you can verify the AI’s work.
2. AI2SQL
AI2SQL is a veteran in this space. It supports a wide range of databases, including MongoDB and MariaDB. It is particularly strong in handling complex JOINs, which is often where lighter SQL AI tools struggle. It acts as a copilot, sitting right next to your code editor.
3. Azure Data Studio (Copilot)
Microsoft has integrated AI for SQL query generation directly into the SQL Server ecosystem. If you are in the Microsoft stack, this is seamless. It uses OpenAI’s models to suggest code completions and entire stored procedures based on the context of your current file.
4. Text2SQL.ai
As the name suggests, Text2SQL.ai is purely focused on the translation layer. It is incredibly fast and great for ad-hoc queries. It’s less of a full “platform” and more of a specialized utility for quick conversions.
5. Google Gemini for BigQuery
Google has integrated its Gemini models directly into BigQuery. This allows for massive scale analysis where you can use natural language to query petabytes of data without worrying about query optimization—the AI handles the partitioning and clustering logic for you.
The Benefits of AI for SQL
Why is everyone rushing to adopt SQL using AI? The ROI is tangible.
- Speed: What used to take 15 minutes to write and debug now takes 15 seconds.
- Accessibility: Marketing managers and HR leads can answer their own questions without pestering the data team.
- Standardization: AI for SQL tools tend to follow best practices (like using readable aliases and standard formatting), which keeps the codebase clean.
- Learning: For beginners, these tools act as an infinite tutor. You can write what you want in English, see the SQL, and learn the syntax in real-time.
The Challenges: It’s Not All Perfect
While text to sql is powerful, it is not without risks. Using text to sql llm systems requires a new type of vigilance.
1. The "Hallucination" Risk
LLMs can sometimes be confidently wrong. An AI for SQL query generator might invent a column that doesn’t exist or assume a relationship between tables that isn’t there. This is why “human in the loop” is still essential. You should never run AI-generated UPDATE or DELETE statements without manual review.
2. Context Windows
Standard LLMs have a limit on how much information they can hold (the context window). If your database has 5,000 tables, you can’t feed the whole schema into the prompt. Advanced SQL AI tools use dynamic context selection to solve this, but it remains a hurdle for massive enterprise data warehouses.
3. Security and Privacy
Sending schema data to a cloud LLM is a concern for many enterprises. The trend in 2026 is moving toward local LLMs, which pair perfectly with lightweight solutions like SQLite database management for secure, isolated environments.
The Future: Agentic Workflows and Vector Databases
As we look toward the end of 2026, AI for SQL is evolving into something even bigger: Agentic Workflows.
Currently, we treat these tools as chatbots: Ask a question, get code. The future is “Agents.” You will give an agent a goal: “Analyze our churn rate for the last year and identify the top 3 contributing factors.”
The Agent will:
- Generate the SQL to pull churn data.
- Execute the query.
- Analyze the results using Python or R.
- Generate a second SQL query to dig deeper into the specific factors (e.g., pricing or support tickets).
- Present a final report.
Furthermore, we will see a merging of Vector Databases and SQL. We won’t just query rows and columns; we will query meanings. You will be able to run SQL queries that filter by “sentiment” or “similarity,” combining traditional structured data with the fuzzy, creative power of AI.
Final Words
The era of Text to SQL is not a fad; it is the new standard for data interaction. Whether you are using SQL AI tools to speed up your workflow or deploying text to SQL LLM architectures to empower your business users, the shift is undeniable.
However, the role of the human expert isn’t disappearing—it’s elevating. The future belongs to those who can orchestrate these AI tools, validate their outputs, and ask the right questions. SQL using AI doesn’t replace the need for data literacy; it rewards it.
Start testing these tools today. The barrier to entry has never been lower, and the power to unlock your data has never been greater.
Recommended Watch
For a deeper technical look at how LLMs and schema understanding actually power these analytics, this video is an excellent resource.
This video from IBM Technology provides a clear explanation of the architecture behind Text-to-SQL systems, specifically visualizing how the LLM interacts with database schemas.